Chinese playing cards

Various types of Money-suited playing cards
Playing cards (Chinese traditional: 紙牌; simplified: 纸牌; pinyin: zhǐpái) were most likely invented in China during the Tang (618-907) or Song dynasty (960-1279). They were certainly in existence by the Mongol Yuan dynasty (1271-1368). Chinese use the word pái (牌), meaning "plaque", to refer to both playing cards and tiles. Many early sources are ambiguous if they don't specifically refer to paper pái (cards) or bone pái (tiles). In terms of game play, there is no difference; both serve to hide one face from the other players with identical backs. Card games are examples of imperfect information games as opposed to Chess or Backgammon.
Michael Dummett attributed to the Chinese the invention of gambling with cards, suits, and trick-taking games. Trick-taking games eventually became multi-trick games. These then evolved into the earliest type of rummy games during the early Qing dynasty (1644-1912). By the end of the monarchy, the vast majority of traditional Chinese card games were of the shedding or fishing variety. Chinese playing cards have proliferated into Southeast Asia by Chinese immigrants. They were also formerly known in Mongolia and Japan. The direction of deals and play is counter-clockwise.
Domino cards
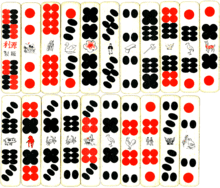
Chinese domino cards with civil suit on top and military on the bottom.
Chinese dominoes first appeared around the Tang or Song dynasty and are derived from all twenty-one combinations of a pair of dice. It is unclear whether they appeared first as cards or as tiles. Though not visually apparent, they are divided into two suits: civil and military. The invention of the concept of suits increased the level of strategy in trick-taking games; the card of one suit cannot beat the card of another suit regardless of its rank.
Domino card decks come in different sizes. Smaller decks are used in trick-taking and banking games. 32-card decks, with the civil suit doubled, are used to play Tien Gow and Pai Gow. Larger decks, for rummy or fishing games, may have well over a hundred cards and can include wild cards.
Money-suited cards
Three-suited Water Margin deck

Six Tigers deck
Money-suited cards have attracted the most attention from scholars. They are considered to be the ancestors of most of the world's playing cards. Each suit represents a different unit of currency. Lu Rong (1436-1494) described a four-suited 38-card deck:
- Cash or Coins: 1 to 9 Cash
- Strings of Cash: 1 to 9 Strings
- Myriads of Strings: 1 to 9 Myriad
- Tens of Myriads: 20 to 90 Myriad, Hundred Myriad, Thousand Myriad, and Myriad Myriad (11 cards in total)
There is no 10 Myriad card as it would share the same name as its suit. By the early 17th-century, the suit of Cash added two more cards: Half Cash and Zero Cash. The Cash suit was also in reverse order with the lower number cards beating the higher. This feature also appeared in other early card games like Ganjifa, Tarot, Ombre, and Maw. During the Ming and Qing dynasties, the suit of Myriads and Tens depicted characters from the novel the Water Margin which is why they were also called Water Margin cards. They were also known as Madiao cards after one of the most popular games.
From at least the 17th-century, games played with stripped decks became more popular. This was done by removing the suit of Tens save for the Thousand Myriad as in the game of Khanhoo. During the 18th and 19th centuries, the Thousand Myriad, Half Cash, and Zero Cash took on new identities as the suitless Old Thousand, White Flower, and Red Flower respectively. They are sometimes joined by a "Ghost" card. During the Qing dynasty, shedding type rummy games became more popular and the 30-card deck was often multiplied with each card having two to five copies. Mahjong, which also exists in card format, was derived from these types of games during the middle of the 19th century.
Four-suited decks still exist and are used by the Hakka to play Six Tigers, a multi-trick game. Six Tigers decks lack illustrations and instead just have ideograms of the rank and suit of each card. Another structurally similar deck is Bài Bất found in Vietnam; it's three-suit version is Tổ tôm. These Vietnamese cards were redesigned by Camoin of Marseilles during French colonial rule to depict people wearing traditional Japanese costumes from the Edo period.
Direct foreign derivatives include Bài tới in Vietnam, Pai Tai in Thailand, Cheki in Malaysia, Singapore, and Indonesia; and possibly Tujeon in Korea. Ultimately, all four-suited decks (especially Italian and Spanish suited packs) are indirectly descended from the money-suited system through Mamluk Kanjifa.
Character cards
Character cards, printed with Chinese characters, first appeared during the middle of the Qing dynasty. There are several types of character cards but are all used to play rummy-like games.
Number cards are quite similar to Six Tigers packs but each deck contains only two suits and includes rank 10. Both suits are labelled in Chinese numerals but one is in normal script while the other is in the financial script. Some decks come with special suitless cards. There are 4 copies of each card.
Wander or Doll cards contain eight series of cards repeated eight times. One card from each series is a special version of the card differentiated from the rest by depicting a human or doll. Each series is marked by one character that when strung together forms a Chinese prayer. Included in each deck is a ninth characterless series with seven cards showing one doll and one card showing two dolls.
Great Man cards are based on a copybook called "On the Great Man" used by students from the Tang to the Qing dynasty. There are 24 or 25 series of cards with each series based on a character from that book. Each series contains four or five identical cards. One variation known as 3-5-7 decks, contain 27 different series but with an uneven number of cards, some have two, three, or five cards with the total being 110 cards.
Unlike other types of Chinese cards, they have not spread to other countries and are largely confined to southern China.
Chess cards
Cards based on Chinese chess appeared during the nineteenth century. They are generally divided into two categories, those with two suits known as Red Cards, and those with four suits known as Four Color Cards. Each suit contains cards named after the seven different chessmen. Some decks have multiple copies of each card and may also contain "gold" wild cards. Most games are rummy-like but Tam cúc in Vietnam is a trick-taking game.
Read more:
COMMENTS








 Various types of Money-suited playing cards
Various types of Money-suited playing cards Chinese domino cards with civil suit on top and military on the bottom.
Chinese domino cards with civil suit on top and military on the bottom. Three-suited Water Margin deck
Three-suited Water Margin deck Six Tigers deck
Six Tigers deck