
- Chess World Cup
- FIDE Grand Prix
- Olympiad
- World Championship
- List of strong tournaments
- List of world championships

- Checkmate patterns
- Chess openings
- Chess strategy
- Chess tactics
- Chess theory
- Endgames
- Pawn structure
- Problems/Compositions












| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |
        |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
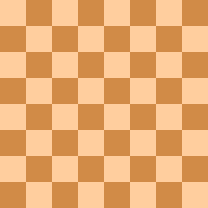
A nightrider (also known as a knightmare or unicorn) is a fairy chess piece that can move any number of steps as a knight in the same direction. Intervening squares must be vacant. For example, a nightrider on b2 can reach square c4 and forward to d6 and e8, but cannot jump over the f4-pawn to reach h5. The nightrider is usually represented by an inverted knight in diagrams, and symbol N in text (in which case the knight is abbreviated as S for German Springer).
The nightrider was invented by T. R. Dawson in 1925, and is mostly used in chess problems.
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |

    |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
The king together with two knights cannot win endgame against a lone king (KSS vs K), but the king together with a knight and a nightrider can win, because the knight cannot win a tempo, but the nightrider can.
Solution: 1. Ne7! Ka7 2. Ng3 Ka8 3. Ne4 Ka7 4. Sb5+ Ka8 5. Nd2#
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |
      |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
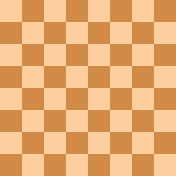
With nightriders on the board, a mutual discovered perpetual check is possible.
A possible continuation would be: 1. Kd3+ Kc5+ 2. Kc3+ Kd5+ 3. Kd3+ Kc5+, etc.
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |

      |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
Nightrider can also participate in triple check.