
- Tabletop games
- Board games
- Tile-based games
- Turn-based games.html
- Abstract strategy games
- card games
- Connection games
- Mancala games
- Paper-and-pencil games
- Word games



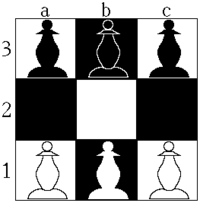 A 3x3 hexapawn board
A 3x3 hexapawn boardHexapawn is a deterministic two-player game invented by Martin Gardner. It is played on a rectangular board of variable size, for example on a 3x3 board or on a chessboard. On a board of size nxm, each player begins with m pawns, one for each square in the row closest to them. The goal of each player is to advance one of their pawns to the opposite end of the board or to prevent the other player from moving.
Hexapawn on the 3x3 board is a solved game; if both players play well, the first player to move will always lose. Indeed, Gardner specifically constructed it as a game with a small game tree, in order to demonstrate how it could be played by a heuristic AI implemented by a mechanical computer. A variant of this game is octapawn.
As in chess, each pawn may be moved in two different ways: it may be moved one square forward, or it may capture a pawn one square diagonally ahead of it. A pawn may not be moved forward if there is a pawn in the next square. Unlike chess, the first move of a pawn may not advance it by two spaces. A player loses if he/she has no legal moves or the other player reaches the end of the board with a pawn.
Whenever a player advances a pawn to the penultimate rank (unless it is an isolated pawn) there is a threat to proceed to the final rank by capture. The opponent's only sensible responses are therefore either to capture the advanced pawn or to advance the threatened one, the latter only being sensible in the case that there is one threatened pawn rather than two. If one restricts 3x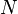 hexapawn with the additional rule that the capture is always compulsory, the result is the game Dawson's chess.
hexapawn with the additional rule that the capture is always compulsory, the result is the game Dawson's chess.
Dawson's chess reduces to the impartial game denoted .137 in Conway's notation. This means that it is equivalent to a Nim-like game in which:
The initial position is a single heap of size 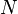 . The nim-sequence for this game is
. The nim-sequence for this game is
0.1120311033224052233011302110452740 1120311033224455233011302110453748 1120311033224455933011302110453748 1120311033224455933011302110453748 1120311033224455933011302110453748 ...,
where bold entries indicate the values that differ from the eventual periodic behavior of the sequence.