
- Chess World Cup
- FIDE Grand Prix
- Olympiad
- World Championship
- List of strong tournaments
- List of world championships

- Checkmate patterns
- Chess openings
- Chess strategy
- Chess tactics
- Chess theory
- Endgames
- Pawn structure
- Problems/Compositions












| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |
              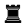    |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
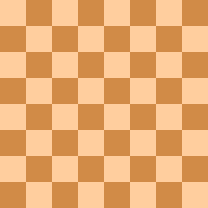
Overloading is a chess tactic in which a defensive piece is given an additional defensive assignment which it cannot complete without abandoning its original defensive assignment.
Krasenkow vs. Karpov, in the first round of the 2003 Corus chess tournament, reached the diagrammed position with Black to play. As the white rook on f1 is tied to the defense of the pawn on f3, Black won immediately with 1...Re1!, overloading the rook: If 2.Rxe1 or 2.Qc4, then 2...Qxf3#. If 2.Kg2, then similarly, 2...Rxf1 3.Kxf1 Qxf3+ and 4...Qxd5.
An overload was also used in Rotlewi versus Rubinstein.
Nisipeanu vs. Giri, 2010| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |

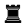    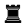                       |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
Liviu-Dieter Nisipeanu vs. Anish Giri, In this position, Giri played 30...Bxh3! overloading the g2 pawn, as 31. gxh3 is met with 31...f3. (32. Re3 Qg5+)