
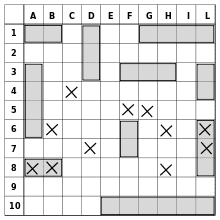
 A map of one player's ships and the hits against them, from a game in progress. The grey boxes are the ships placed by the player, and the cross marks show the squares that their opponent has fired upon. The player would be tracking the success of their own shots in a separate grid.
A map of one player's ships and the hits against them, from a game in progress. The grey boxes are the ships placed by the player, and the cross marks show the squares that their opponent has fired upon. The player would be tracking the success of their own shots in a separate grid.Battleship (also Battleships or Sea Battle) is a guessing game for two players. It is known worldwide as a pencil and paper game which dates from World War I. It was published by various companies as a pad-and-pencil game in the 1930s, and was released as a plastic board game by Milton Bradley in 1967.
The game of Battleship is thought to have its origins in the French game L'Attaque played during World War I, although parallels have also been drawn to E. I. Horseman's 1890 game Baslinda, and the game is said to have been played by Russian officers before World War I. The first commercial version of the game was Salvo, published in 1931 in the United States by the Starex company. Other versions of the game were printed in the 1930s and 1940s, including the Strathmore Company's Combat: The Battleship Game, Milton Bradley's Broadsides: A Game of Naval Strategy and Maurice L. Freedman's Warfare Naval Combat. Strategy Games Co produced a version called Wings which pictured planes flying over the Los Angeles Coliseum. All of these early editions of the game consisted of pre-printed pads of paper.
In 1967 Milton Bradley introduced a version of the game that used plastic boards and pegs. The method of play involved using pegboards and miniaturized plastic ships, and was thought of by Ed Hutchins. In 1977, Milton Bradley also released a computerized Electronic Battleship, followed in 1989 by Electronic Talking Battleship. In 2008, an updated version of Battleship was released, using hexagonal tiles. In the updated version, each player's board contains several islands on which "captured man" figurines can be placed. Ships may be placed only around the islands, and only in the player's half of the board. When the movie "Battleship" was released, the board game reverted back to the original 1967 style. The 2008 updated version is still available as "Battleship" Islands".
Battleship was one of the earliest games to be produced as a computer game, with a version being released for the Z80 Compucolor in 1979. Many computer editions of the game have been produced since. In Clubhouse Games for the Nintendo DS, Battleship is known as Grid Attack. It is played on an 8x8 grid, and includes slight variations, such as 4-player gameplay, various ship sizes and shapes, as well as the option to make the ships touch each other. Iterations of Battleship appear as applications on numerous social networking services.
Battleship was also part of Hasbro Family Game Night for the PlayStation 2 and Wii, as well as the Xbox 360 (Xbox Live Arcade). These alter the rules, including the size of the grid (8x12 in the NES version, 8x8 in the Game Boy version), size of ships (it is common to feature a submarine that takes up a single square) and special shot missiles for each ship (for example, in the NES version the cruiser has a 5-shot missile which strikes 5 squares in an X pattern on the grid in one turn. Submarine-tracking sonar and aerial reconnaissance to spot ships are also features).
A minigame version of the game was used in the third season of The Hub's Family Game Night, which uses a 5x5 grid and the first team to sink three ships wins the game.
The 2012 film Battleship is an American science fiction action movie inspired by the board game.
 A typical pen-and-paper version of the game, showing the large "primary" grid and the smaller "tracking" grid
A typical pen-and-paper version of the game, showing the large "primary" grid and the smaller "tracking" gridThe game is played on four grids, two for each player. The grids are typically square - usually 10x10 - and the individual squares in the grid are identified by letter and number. On one grid the player arranges ships and records the shots by the opponent. On the other grid the player records his/her own shots.
Before play begins, each player secretly arranges their ships on their primary grid. Each ship occupies a number of consecutive squares on the grid, arranged either horizontally or vertically. The number of squares for each ship is determined by the type of the ship. The ships cannot overlap (i.e., only one ship can occupy any given square in the grid). The types and numbers of ships allowed are the same for each player. These may vary depending on the rules.
There are two typical complements of ships, as given in the Milton Bradley version of the rules:
| Type of ship | Size |
|---|---|
| Aircraft carrier | 5 |
| Battleship | 4 |
| Submarine | 3 |
| Destroyer (or Cruiser) | 3 |
| Patrol boat (or destroyer) | 2 |
After the ships have been positioned, the game proceeds in a series of rounds. In each round, each player takes a turn to announce a target square in the opponent's grid which is to be shot at. The opponent announces whether or not the square is occupied by a ship, and if it is a "miss", the player marks their primary grid with a white peg; if a "hit" they mark this on their own primary grid with a red peg. The attacking player notes the hit or miss on their own "tracking" grid with the appropriate color peg (red for "hit", white for "miss"), in order to build up a picture of the opponent's fleet.
When all of the squares of a ship have been hit, the ship is sunk, and the ship's owner announces this (e.g. "You sank my battleship!"). If all of a player's ships have been sunk, the game is over and their opponent wins.
| Type of ship | Size | Number per player |
|---|---|---|
| battleship (Russian: линкор)/four-decker (Russian: четырёхпалубник)/four-funnel (Russian: четырёхтрубный) | 4 | 1 |
| cruiser (Russian: крейсер)/three-decker (Russian: трёхпалубник)/three-funnel (Russian: трёхтрубный) | 3 | 2 |
| destroyer (Russian: эсминец)/two-decker (Russian: двухпалубник)/two-funnel (Russian: двухтрубный) | 2 | 3 |
| submarine (Russian: подводная лодка)/single-decker (Russian: однопалубник)/single-funnel (Russian: однотрубный) | 1 | 4 |