
- Chess World Cup
- FIDE Grand Prix
- Olympiad
- World Championship
- List of strong tournaments
- List of world championships

- Checkmate patterns
- Chess openings
- Chess strategy
- Chess tactics
- Chess theory
- Endgames
- Pawn structure
- Problems/Compositions












In chess the fianchetto (Italian: "little flank") is a pattern of development wherein a bishop is developed to the second rank of the adjacent knight file, the knight pawn having been moved one or two squares forward.
The fianchetto is a staple of many "hypermodern" openings, whose philosophy is to delay direct occupation of the center with the plan of undermining and destroying the opponent's central outpost. It also regularly occurs in Indian defences. The fianchetto is less common in open games (1.e4 e5) but the king's bishop is sometimes fianchettoed by Black in the Spanish Game or by White in an uncommon variation of the Vienna Game.
One of the major benefits of the fianchetto is that it often allows the fianchettoed bishop to become more active. Because the bishop is placed on one of the two longest diagonals (either h1-a8 or a1-h8), it controls the maximum possible number of squares and can become a powerful offensive weapon. However, a fianchettoed position also presents some opportunities for the opposing player: if the fianchettoed bishop can be exchanged, the squares the bishop was formerly protecting will become weak (see hole) and can form the basis of an attack (particularly if the fianchetto was performed on the kingside). Therefore, exchanging the fianchettoed bishop should not be done lightly, especially if the enemy bishop of the same colour is still on the board.
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |
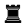      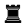                          |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
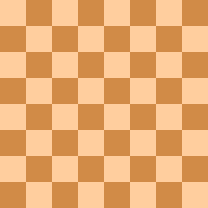
The diagram to the right shows three different sorts of fianchetto (not as part of an actual game, but as separate examples that have been collapsed into a single chessboard). White's king's bishop is in a regular fianchetto, with the knight-pawn advanced one square and the bishop occupying the long diagonal. This is by far the most common type of fianchetto, seen in the Sicilian Dragon, Pirc Defence, Modern Defence, Modern Benoni, Grünfeld Defence and King's Indian Defence, among other openings.
Black's queen's bishop is also fianchettoed, but the knight pawn has moved forward two squares, making this a long fianchetto. The b-pawn also controls the c4 square, which is often advantageous. If White plays the King's Indian Attack 1.Nf3 2.g3, Black may play a long queen's fianchetto to oppose White's bishop and make it more difficult for White to play a c4 pawn break. The long fianchetto on the kingside is more rarely played, because it weakens the pawn shield in front of the castled position, and controls a less important square. Nevertheless, Grob's attack 1.g4?! and the Borg Defence ("Grob" backwards) 1.e4 g5?! are sometimes played by players like International Master Michael Basman.
White's queen's bishop has moved out to a3 in what is sometimes called an extended fianchetto. Rather than control the long diagonal, it takes aim at Black's f8 square. If Black moves his e-pawn, White can play Bxf8, after which Black will have to waste time on artificial castling after recapturing with his king. This tactic is often seen in the Evans Gambit, and gives the Benko Gambit much of its bite. Black often plays Ba6 in the French Defence, and the Queen's Indian Defence if White plays g3 in order to fianchetto his own bishop (Aron Nimzowitsch's move against the Classical variation).
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
| 8 |

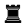   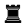                           |
8 | |||||||
| 7 | 7 | ||||||||
| 6 | 6 | ||||||||
| 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| 3 | 3 | ||||||||
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||
| 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | ||
Rubinstein vs. Nimzowitsch, Marienbad 1925 has four fianchettoed bishops; two knights are developed, and two remain on their home square. At this position, Nimzowitsch humorously points out (in My System): "Each side castles now with a clear conscience, for not even the most hypermodern pair of masters can produce more than four fianchettoed Bishops!"